

Table of Contents
In the modern world, where everything moves quickly, it is often hard to keep a healthy lifestyle. However, one of the most crucial aspects of achieving overall well-being is understanding nutrition and dietetics. This comprehensive guide will delve into what nutrition is, its importance, signs of good and poor nutritional status, and the Food Guide Pyramid to help you make informed dietary choices.
What is nutrition
Nutrition is the way your body receives food and uses it for growth, energy and health. In the field of nutrition and dietetics, this process is the base of a healthy life. When you eat the right nutrients, your body repairs tissues, stays strong and prevents diseases. Good nutrition supports every function of the body in a simple and natural way.
Macronutrients: The Building Blocks
Macronutrients are the foundation of nutrition and dietetics.
Proteins help repair muscles, support body structure and make enzymes and hormones.
Carbohydrates give energy for the brain and muscles.
Fats support energy storage protect organs and help in hormone production.
Micronutrients: The Essential Catalysts
Micronutrients are also an important part of nutrition and dietetics.
Vitamins help the body perform many actions. Vitamin C supports immunity and Vitamin D helps in calcium absorption.
Minerals like calcium, potassium and iron support bone strength, fluid balance and oxygen transport.
Importance of Nutrition
Good nutrition is crucial for several reasons:
Supports Growth and Development
Adequate nutrition is vital for the growth of children and the healthy development of pregnant women. Nutrients like calcium and vitamin D are essential for bone growth, while proteins are necessary for muscle development.
Boosts Immune System
A balanced diet helps the body fight infections. Vitamins C and D and zinc play an important role in keeping the immune system strong.
Prevents Chronic Diseases
A balanced diet reduces the risk of chronic conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, and certain cancers. Consuming whole grains, lean proteins, and plenty of fruits and vegetables can help maintain optimal health and prevent disease onset.
Maintains Healthy Weight
Good nutrition helps regulate body weight and prevents obesity, which is linked to various health issues like hypertension, diabetes, and joint problems. Balanced caloric intake and regular physical activity are key to maintaining a healthy weight.
Enhances Mental Health
Nutrients like omega-3 fatty acids are associated with improved mood and cognitive function, potentially reducing the risk of depression and anxiety. A well-nourished brain can better manage stress and maintain mental clarity.
Signs of Good Nutritional Status
Good nutritional status is a major goal of nutrition and dietetics.
Below are several indicators suggesting that you are moving along the right path.
Healthy Body Weight
Maintaining a weight within the recommended range for your height and age indicates that you are receiving the right balance of nutrients. A healthy body weight reduces the risk of various diseases and promotes longevity.
Balanced Energy Levels
Consistent energy throughout the day without excessive fatigue suggests that your diet provides adequate calories and nutrients to meet your body’s needs.
Healthy Skin and Hair
Clear skin and strong, healthy hair are visible signs of good nutrition. Vitamins and minerals, such as Vitamin E and biotin, contribute to skin and hair health.
Regular Bowel Movements
A diet rich in fiber promotes digestive health, leading to regular bowel movements and preventing constipation or other digestive issues.
Strong Immune Response
Fewer illnesses and quicker recovery from infections suggest a robust immune system, which is often a result of proper nutrient intake.
Signs of Poor Nutritional Status
On the flip side, poor nutritional status can lead to various health problems.
The following indicators should be observed:
Unexplained Weight Loss or Gain
Significant changes in weight can indicate nutritional deficiencies or excesses. Unintentional weight loss might suggest inadequate nutrient intake, while sudden weight gain could be a sign of excessive calorie consumption.
Fatigue and Weakness
Low energy levels may signal inadequate nutrient intake, particularly deficiencies in iron, vitamin B12, or other essential vitamins and minerals.
Frequent Illness
A weakened immune system can lead to increased susceptibility to infections. Frequent illnesses may be a sign that your body is not receiving the necessary nutrients to support immune function.
Skin and Hair Problems
Dry skin, hair loss, or brittle nails can indicate deficiencies in essential nutrients like vitamins A, C, D, E, and minerals such as zinc and selenium.
Digestive Issues
Problems like constipation or diarrhea may arise from poor dietary choices, such as insufficient fiber intake or excessive consumption of processed foods.
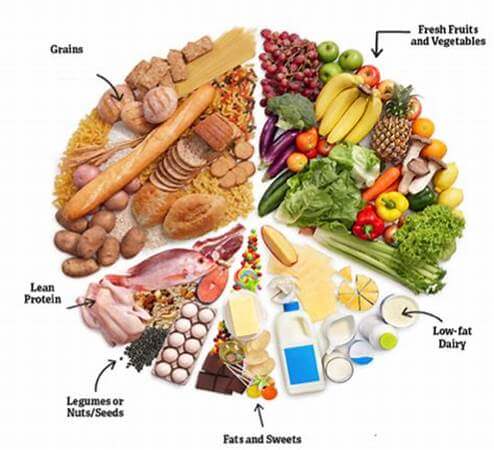
Understanding the Food Guide Pyramid

The Food Guide Pyramid is a simple tool used in nutrition and dietetics. It shows how much of each food group you should eat.
Grains: The Base of the Pyramid
Grains form the foundation of the pyramid, recommending whole grains as the primary source of carbohydrates. Whole grains like brown rice, whole wheat bread, and oats provide essential fiber, vitamins, and minerals.
Fruits and Vegetables
Encouraged in large amounts, fruits and vegetables are rich in vitamins, minerals, and fiber. They help reduce the risk of chronic diseases and support overall health. Make sure to have a variety of colors and food types to boost your nutrient intake.
Proteins
Includes lean meats, fish, beans, and nuts, recommended in moderation. Proteins are vital for repairing muscles, supporting your immune system and overall growth. Opt for lean sources like chicken, turkey, tofu, and legumes to maintain a healthy diet.
Dairy
Low-fat or fat-free options are suggested for calcium and vitamin D. Dairy products like milk, yogurt, and cheese support bone health and provide essential nutrients necessary for various bodily functions.
Fats and Sweets
These should be consumed sparingly, focusing on healthy fats such as those found in avocados, nuts, and olive oil. Limit the intake of saturated and trans fats, as well as sugary foods and beverages, to maintain optimal health.

The Role of Dietetics
Dietetics is the practical side of nutrition and dietetics. It teaches how food choices affect health.
Personalized Diet Plans
Dietitians tailor diet plans based on individual needs, considering factors like age, gender, health status, and lifestyle. This personalized approach ensures that each person receives the right balance of nutrients to support their unique health goals.

Managing Medical Conditions
Proper diet management is essential for conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, and celiac disease. Dietitians work with patients to develop dietary strategies that help control symptoms and improve quality of life.
Promoting Healthy Eating Habits
Educating individuals about the importance of balanced diet and how to make healthier food choices is a key aspect of dietetics. This empowerment leads to long-term health benefits and prevents the onset of diet-related diseases.

Addressing Malnutrition
Malnutrition is characterized by deficiencies, surpluses, or imbalances in an individual’s energy and/or nutrient intake. It can lead to a variety of health issues, from stunted growth in children to increased susceptibility to diseases in adults.
Types of Malnutrition
Undernutrition: Results from inadequate intake of nutrients, leading to weight loss, muscle wasting, and impaired immune function.
Overnutrition: Caused by excessive intake of nutrients, particularly calories, leading to obesity and related health problems.
Micronutrient Deficiencies: Lack of essential vitamins and minerals, such as iron deficiency anemia or vitamin D deficiency.

Preventing Malnutrition
Prevention involves ensuring access to a balanced diet rich in essential nutrients. Public health initiatives, education on dietary habits and support for vulnerable populations are critical in combating malnutrition globally.
Enhancing Nutritional Status
Achieving and maintaining a good nutritional status involves several strategies:
Balanced Diet
Consume a variety of foods from all food groups to ensure a comprehensive intake of nutrients. Emphasize whole grains, lean proteins, fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats.
Portion Control
Managing portion sizes helps maintain a healthy weight and prevents overeating. Understanding serving sizes and listening to your body’s hunger cues are important aspects of portion control.
Regular Physical Activity
Exercise complements good nutrition by helping to regulate weight, improve cardiovascular health, and enhance overall well-being.
Hydration
Adequate water intake is essential for digestion, nutrient transport, and maintaining body temperature. Aim to drink at least eight glasses of water a day, adjusting based on activity level and climate.
Limit Processed Foods
Minimize consumption of processed and sugary foods, which are often high in unhealthy fats, sugars, and sodium. Opt for whole, unprocessed foods to maximize nutrient intake.

Practical Tips for a Balanced Diet
Implementing a balanced diet can seem daunting, but here are some practical tips to make it easier:

Plan Your Meals
Take time each week to plan your meals. This helps ensure a balanced intake of nutrients and reduces the likelihood of unhealthy last-minute food choices.
Read Food Labels
Understanding food labels helps you make informed decisions about what you’re eating. Pay attention to serving sizes, calorie content, and the presence of added sugars and unhealthy fats.
Cook at Home
Cooking at home gives you the ability to choose your ingredients and cooking techniques, which simplifies the process of adhering to a healthy diet.
Incorporate Variety
Eating a wide range of foods ensures that you receive all the necessary nutrients. Experiment with different fruits, vegetables, grains, and proteins to keep your diet interesting and nutritious.
Snack Smartly
Select wholesome snacks like fruits, nuts, or yogurt in place of processed alternatives. Consuming healthy snacks can stabilize your energy and help you avoid excessive eating during meals.
Dietitian’s Desk

The field of nutrition and dietetics helps you understand how food affects your health. When you follow balanced meals, stay hydrated, stay active and avoid processed foods, your body becomes stronger from the inside. Good nutrition supports immunity, energy, mood, and long-term health. Your journey to a healthy life begins with simple daily choices that nourish the body.
By applying the knowledge of nutrition and dietetics, you create a healthier and happier future for yourself.
Further Reading and Resources
By staying informed and proactive about your nutritional choices, you can pave the way for a healthier future. Here are some valuable resources to expand your knowledge on nutrition and dietetics:
- Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics
- World Health Organization (WHO) Nutrition
- Healthy Diet Initiative by WHO
- National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences (NIEHS)
- Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health
- Dt. Anup Agharwal’s Nutrition Courses
FAQs
What is nutrition?
It is the process by which living organisms obtain and utilize food to support bodily functions, growth, and overall health. It involves the intake of essential nutrients, including macronutrients (proteins, carbohydrates, and fats) and micronutrients (vitamins and minerals), to maintain optimal health and prevent disease.
Why is nutrition important?
Because it supports growth and development, enhances the immune system, prevents chronic diseases, maintains healthy body weight, and improves mental health. Proper nutrition ensures that the body functions efficiently and reduces the risk of developing health issues.
Can a balanced diet prevent chronic diseases?
Yes. A balanced diet can reduce the risk of chronic conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, and certain types of cancer.
Is it necessary to include all food groups in my diet?
Yes. Including a variety of food groups ensures a comprehensive intake of essential nutrients, promoting overall health.
Are there visible signs of good nutritional status?
Yes. Signs of good nutritional status include maintaining a healthy body weight, clear skin, strong hair, and consistent energy levels.
Can poor nutrition lead to frequent illness?
Yes. Poor nutrition can weaken the immune system, making the body more susceptible to infections and illnesses.
Is dietetics the same as nutrition?
No. While closely related, dietetics focuses on applying nutritional principles to improve health through diet, often involving personalized meal plans and managing medical conditions.
What is malnutrition?
Malnutrition refers to the condition that occurs when a person’s diet lacks essential nutrients or has an imbalance of nutrients, leading to health problems. It can manifest as undernutrition (deficiency of nutrients) or overnutrition (excessive intake of nutrients) and can cause issues like stunted growth, weakened immunity, and increased susceptibility to diseases.
How can I improve my nutritional status?
Improving nutritional status involves consuming a balanced diet with a variety of foods from all food groups, practicing portion control, staying hydrated, engaging in regular physical activity, and limiting the intake of processed foods. Consulting a dietitian can also help in creating a personalized nutrition plan tailored to individual needs.
What role do micronutrients play in health?
Micronutrients, including vitamins and minerals, play a crucial role in health by supporting various bodily functions. For example, Vitamin C boosts the immune system, calcium strengthens bones, and iron aids in oxygen transport. While they are required in smaller amounts compared to macronutrients, their impact on health is significant.

🎯 10+ years of Experience
🎓 10k+ Trained ( 📍 Jaipur )
💪 Helping change people’s lives
🌿 Most trusted lifestyle counselor
