
Table of Contents

A healthy digestive system is essential to your overall health and well-being, and incorporating specific foods after each meal can significantly enhance your digestion. Choosing foods for better digestion not only aids in reducing discomfort but also supports optimal nutrient absorption. In this blog, we’ll explore six powerful, natural foods that can aid in digestion, reduce discomfort, and even improve nutrient absorption. Want to avoid common food pairing mistakes that harm your digestion? Check out these 12 harmful food combinations to avoid.
Understanding Digestion
Digestion is the complex process through which our body breaks down food and extracts nutrients. From the moment we eat, a series of mechanical and chemical processes occur, breaking down the food and absorbing nutrients through the digestive tract. Poor digestion can lead to discomfort, bloating, and even nutrient deficiencies over time. Thankfully, adding specific foods after meals can ease digestion, balance gut bacteria, and prevent digestive issues.
6 Best Foods for Better Digestion After Each Meal
Here are six foods with unique digestive benefits to include after every meal:
Ginger
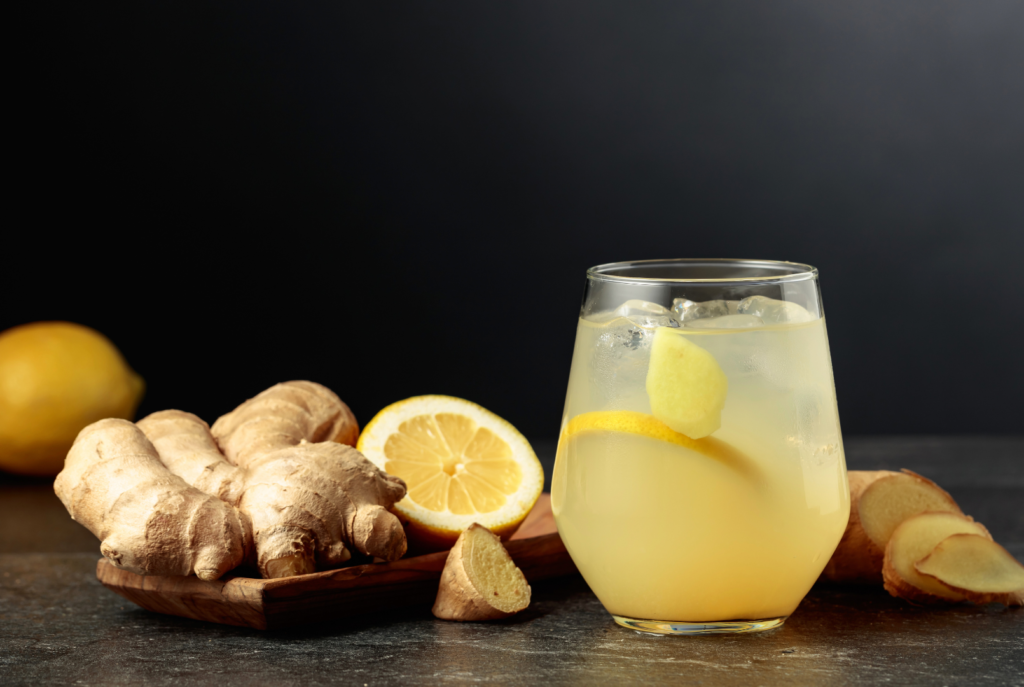

Ginger has been prized for centuries for its digestive benefits. Its active components, like gingerol, have anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties that reduce bloating and indigestion.
Benefits and Importance:
- Reduces Nausea: Ginger is highly effective in preventing nausea and reducing bloating, helping food to pass smoothly through the stomach.
- Stimulates Digestion: It promotes digestive enzymes that break down food more effectively, aiding in faster digestion.
Tip: Add a small piece of fresh ginger, or sip on ginger tea after your meal to soothe your stomach.
Curd (Yogurt)
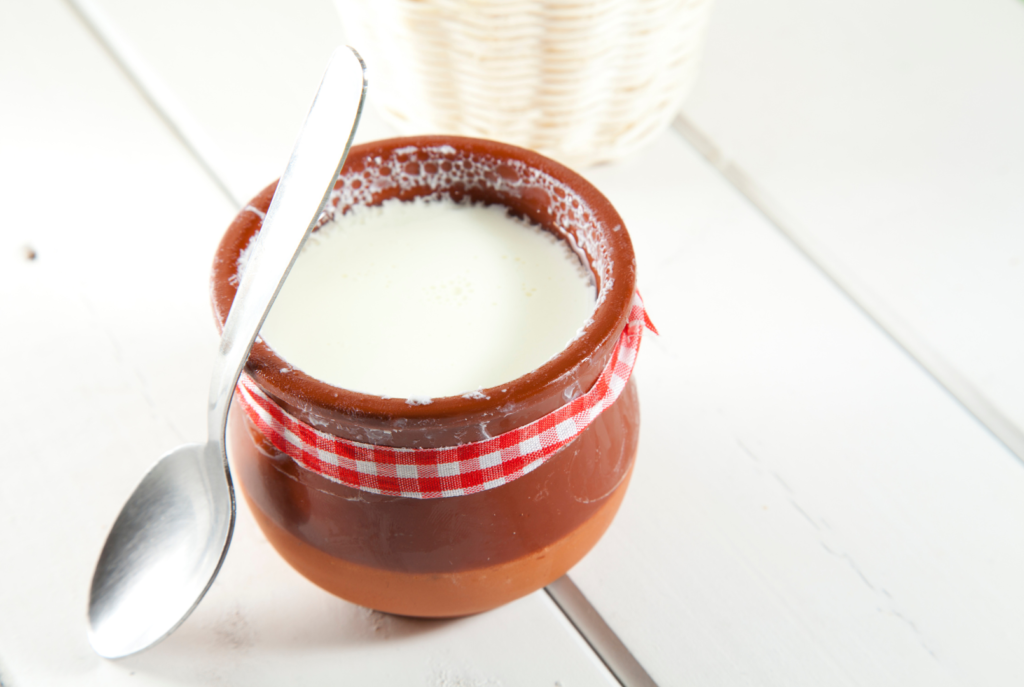

Curd is a natural probiotic, full of beneficial bacteria that support gut health and improve digestion. Eating curd regularly after meals can prevent bloating and help maintain a healthy balance of gut flora.
Benefits and Importance:
- Rich in Probiotics: The good bacteria in curd can prevent harmful bacteria from upsetting the digestive balance.
- Supports Lactose Digestion: Curd contains enzymes that help break down lactose, making it an ideal post-meal choice for those with mild lactose intolerance.
Tip: Have a small serving of curd with a pinch of black salt after your meal for better digestion.
Looking for protein options that don’t mess with your gut? Try these 6 Protein-Rich Foods That Don’t Cause Bloating.

Fennel Seeds
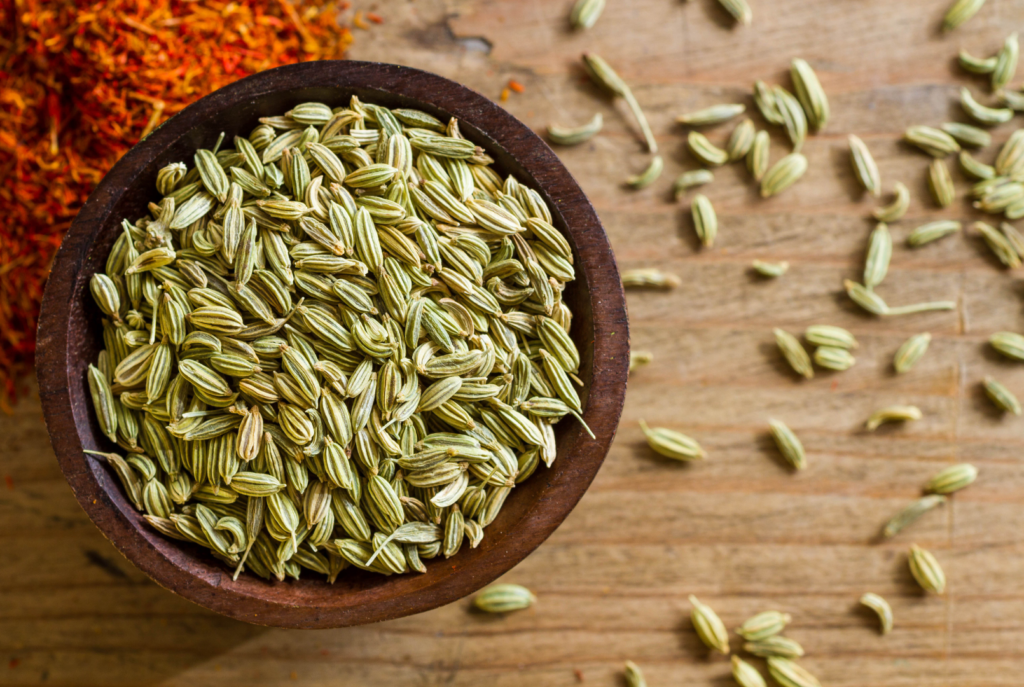

Fennel seeds are popular in Indian cuisine as a post-meal digestive aid. Their anethole compound relaxes the muscles in the digestive tract, providing quick relief from gas and bloating.
Benefits and Importance:
- Alleviates Bloating: Fennel seeds work wonders to alleviate bloating and ease stomach discomfort.
- Prevents Indigestion: They stimulate the secretion of digestive juices, preventing indigestion and heartburn.
Tip: Chew a small teaspoon of fennel seeds after meals for instant freshness and digestive relief.
Jaggery and Cumin (Gur + Jeera)
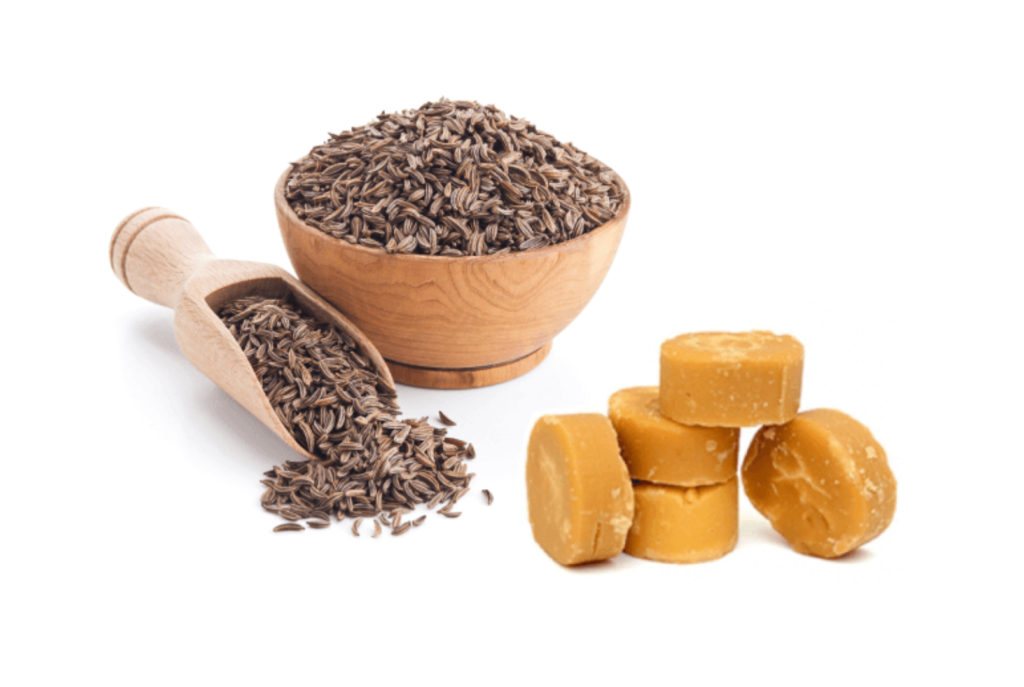

A mixture of jaggery (gur) and cumin (jeera) is a classic remedy for improving digestion and promoting gut health. Jaggery helps to cleanse the digestive system, while cumin has anti-inflammatory properties that aid in digestion.
Benefits and Importance:
- Boosts Digestion: The sweet and mildly spicy combination stimulates digestive enzymes, speeding up digestion.
- Reduces Acidity: Both jaggery and cumin help neutralize stomach acids, preventing acid reflux and bloating.
Tip: Consume a small piece of jaggery with a pinch of roasted cumin powder for a delicious and effective digestive aid.
Mint (Pudina)
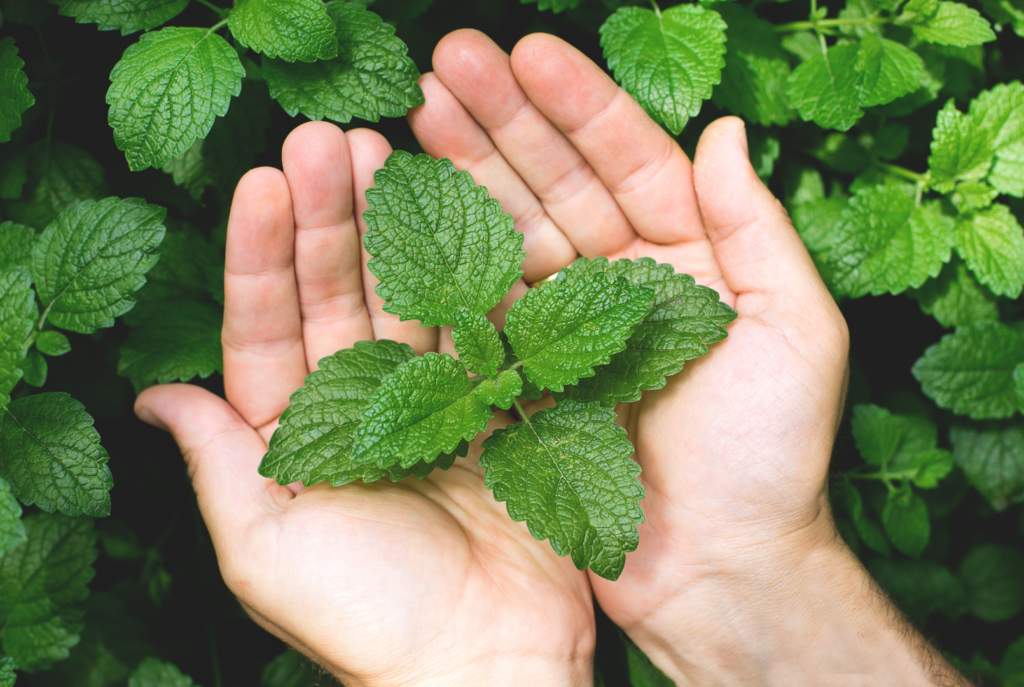

Mint is another fantastic post-meal food that can improve digestion. The menthol in mint leaves has a soothing effect on the stomach muscles, which helps prevent cramping and indigestion.
Benefits and Importance:
- Soothes Stomach Lining: Mint calms the stomach muscles and helps food move smoothly through the digestive tract.
- Reduces Irritable Bowel Symptoms: Its anti-spasmodic properties make it beneficial for people with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS).
Tip: Drink a glass of water infused with mint leaves, or have fresh mint leaves as a mouth freshener post-meal.
Dark Chocolate
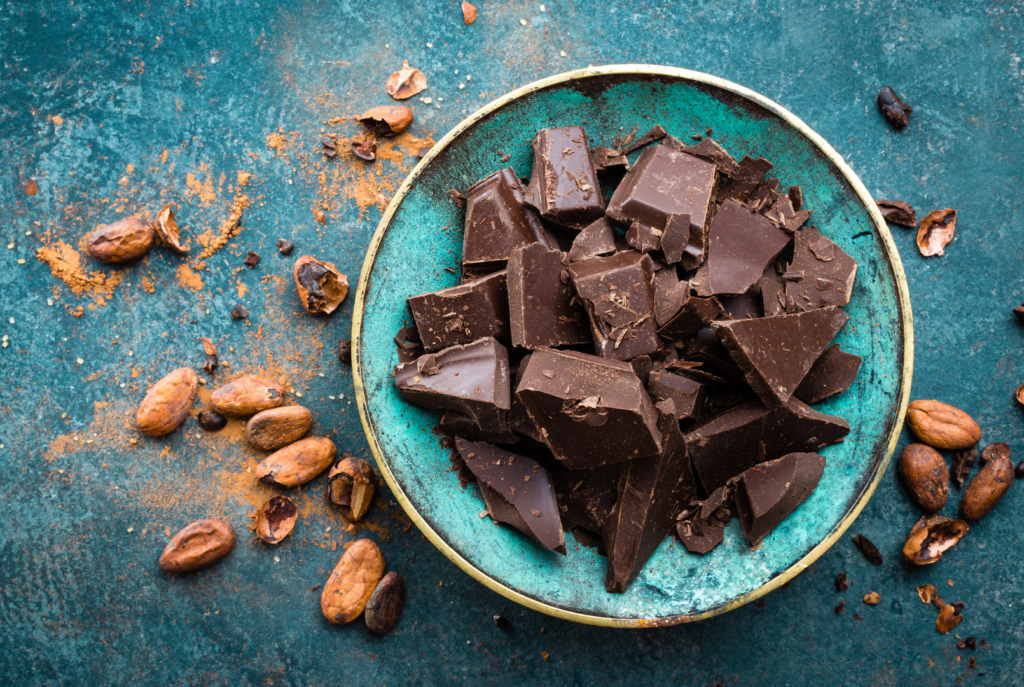

Surprisingly, dark chocolate (in moderation) can be beneficial for digestion. The high cacao content in dark chocolate stimulates the production of digestive enzymes, which can improve nutrient absorption.
Benefits and Importance:
- Rich in Fiber: Dark chocolate provides fiber that supports digestive health and encourages the growth of good gut bacteria.
- Prevents Inflammation: Its antioxidants help reduce gut inflammation, which can be beneficial for those with inflammatory bowel issues.
Tip: Opt for dark chocolate with at least 70% cacao to enjoy digestive benefits without added sugars.
Want a crunchy post-meal option that supports digestion too?
Discover the Digestive Power of Roasted Chana.
Bonus Tip: Water Intake After Meals

It’s a common question: Is it better to drink water immediately after meals, or should you wait? Experts generally recommend waiting around an hour after meals before drinking water, as it allows the digestive process to start undisturbed. Drinking warm or hot water post-meal is believed to help break down food and ease digestion, especially for those with a slower metabolism.
Dt. Anup Agharwal recommends a warm cup of water after an hour of eating to facilitate smoother digestion.
Dietitian’s Desk
Integrating these foods into your diet after meals can contribute to healthier digestion and better nutrient absorption. Each food—from ginger to dark chocolate—offers unique benefits that support gut health, reduce bloating, and enhance the digestive process.
Dt. Anup Agharwal suggests, “A simple addition of these foods post-meal can go a long way in preventing digestive discomfort and enhancing nutrient absorption, paving the way for overall better health.”Tip: Opt for dark chocolate with at least 70% cacao to enjoy digestive benefits without added sugars.
FAQs
Why is it important to eat specific foods after meals for digestion?
Eating specific foods post-meal can aid digestion by stimulating digestive enzymes, reducing bloating, and enhancing nutrient absorption, making the digestive process smoother and more efficient.
How does ginger help with digestion after meals?
Ginger contains gingerol, which has anti-inflammatory properties that help reduce nausea and bloating, stimulate digestion, and allow food to pass smoothly through the stomach.
What are the benefits of eating curd after a meal?
Curd is rich in probiotics that promote a healthy balance of gut bacteria, which can prevent digestive discomfort, reduce bloating, and improve nutrient absorption, especially for those who are mildly lactose intolerant.
Can fennel seeds really reduce bloating?
Yes, fennel seeds contain compounds like anethole that help relax muscles in the digestive tract, preventing gas, alleviating bloating, and offering quick digestive relief.
Why is the combination of jaggery and cumin recommended post-meal?
Jaggery helps cleanse the digestive tract, while cumin has anti-inflammatory properties that aid in digestion, reduce acidity, and prevent bloating when taken together.
What makes mint effective for digestion?
Mint contains menthol, which relaxes the stomach muscles and soothes the stomach lining, making it helpful for people who experience cramping, indigestion, or irritable bowel syndrome.
Is dark chocolate really good for digestion?
In moderation, dark chocolate with a high cacao content (70% or more) can stimulate digestive enzymes, provide fiber for gut health, and help reduce inflammation in the digestive system.
Should I drink water right after a meal?
It’s better to wait about an hour before drinking water to allow the stomach to begin the digestive process. Drinking warm water afterward can aid digestion, especially for those with slower metabolism.
Can these foods help with long-term digestive health?
Yes, consistently including these foods after meals can promote a healthier digestive system, improve gut health, and reduce issues like bloating and indigestion over time.
What does Dt. Anup Agharwal recommend for better digestion?
Dt. Anup Agharwal suggests including natural, digestive-friendly foods like ginger, curd, or mint after meals to ease digestion and improve nutrient absorption, supporting long-term gut health.

🎯 10+ years of Experience
🎓 10k+ Trained ( 📍 Jaipur )
💪 Helping change people’s lives
🌿 Most trusted lifestyle counselor
